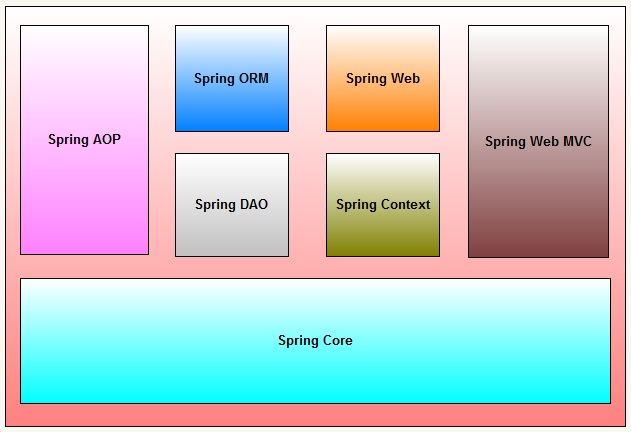
Spring Dependency Injection
Spring uses inversion of control the dependencies between objects. Traditional approach before Spring framework was to hard code the dependencies and this creates tightly coupled code and there was no easy way to change that. People used to minimize this tight coupling, by resorting to ” programming to an interface and not to an implementation”, but even with that approach, the actual creation of the dependent object was the responsibility of the calling piece of code. Of course there were custom frameworks being developed by various individuals to create some form of inversion of control to achieve dependency injection ( DI). Spring changed all that by incorporating dependency injection in a framework.
Lets take example of Employee object
class Employee
{
int empId;
String empName
}
Here when we wish to create object Employee, the Employee object creation is dependent on values of empId and empName i.e.
Employee e1=new Employee(1,"Vikas");
These values need to be hard coded in the program as stated earlier. The scenario becomes still tough when we have the concept of containment in class like :
class Date
{
int
dd,mm,yy;
Date(int
dd,int mm,int yy)
{
this.dd=dd;
this.mm=mm;
this.yy=yy;
}
}
And
class Employee
{
Date dt_of_join;
Int empId;
String empName;
Employee(int empId,String empName,Date dt_of_join)
{
this.dt_of_join=dt_of_join;
this.empId=empId;
this.empName=empName
}
}
Here Employee object is also dependent on object of Date. So, to create object of Employee, one need to create Date object and then push it into Employee object
i.e.
Date d1=new Date(10,12,1989);
Employee e1=new Employee(1,"Vikas",d1)
This traditional way of creating and pushing objects is very difficult for maintenance of application. So we are in need of a concept called as DI.
Dependency Injection (DI) – Spring
In Spring framework, Dependency Injection (DI) is used to satisfy the dependencies between objects. It exits in two major types :
- Constructor Injection
- Setter Injection
Dependency Injection offers atleast the following advantages
- Loosely couple code
- Separation of responsibility
- Configuration and code is separate
In next session we will start with the first program of Spring DI with Setter Injection